Cheque bouncing in India can occur for various reasons. However, you must file a criminal case if it becomes an offence. In this article, you will know the time duration to get a final judgement and the procedure to file a case against a cheque bounce in India
Cheque bounce cases in India are considered equivalent to criminal cases. The cheque bounce can happen due to any number of reasons. But when the reason becomes a purposeful offense, it becomes a criminal case. Know about Court Judgment on a Cheque Bounce Case.
Cheque bouncing can happen for many reasons. However, you will have to file a criminal case when it becomes an offense. Initially, the drawee’s bank issues a cheque-bouncing memo. But if it continues for other reasons apart from the usual reasons, a bouncing case can be filed against the drawee. Further, they may have to go through a tough court procedure. In this article, you will know, how to file a case against a cheque bounce.
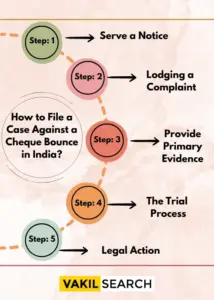
How to File a Case Against a Cheque Bounce in India?
In case a cheque gets bounced for other reasons apart from the usual reasons, then as per section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act of 1881. The payee can file a civil or criminal case for the same. Moreover, they can follow the step-by-step procedure of the same that are mentioned below:
-
Step 1: Serve a Notice
The first step to filing a case against cheque bounce case is to serve the Legal Notice Draft to the drawee. The notice can be sent through a registered post or speed post.
The purpose of issuance of the legal notice to the drawee is to ensure that the individual understands the cause of the cheque bounce. For instance, if the bounce has occurred due to insufficient funds in the drawer’s account, they can rectify the same.
-
Step 2: Lodging a Complaint
The second step for proceeding toward the bouncing case is to complain with the help of an experienced lawyer. As per the second step, the drawee against whom the complaint has been registered has to appear before the court. In case the drawee is innocent, then they have to prove their innocence and seek bail from the court.
-
Step 3: Provide Primary Evidence
Thirdly, the payee has to provide the primary evidence to prove that the cheque has indeed bounced due to the negligence of the drawee. For instance, the payee can present the memo from the drawee’s bank, and the record of a notice served to the drawee. The purpose of the same is to ensure that the drawee pays the amount to the payee as per the bounced cheque.
-
Step 4: The Trial Process
The next process is following the trial process. The trial process for the bouncing case is done as per section 138 of the National Instruments Act of India. The payee submits the evidence to support their case, and the drawee can cross-examine the evidence. Further, try to prove their innocence.
-
Step 5: Legal Action
The final step of the bouncing case is the punishment the court declares after completing the entire hearing process. 2-year sentence and a penalty, which is twice the amount mentioned in the bounced cheque. Thus, these are the step-by-step procedures for the Court Judgment on the Cheque Bounce Case.
What Is the Structure of Payment of Court Process Fees?
Every legal process in the court requires payment of court fees. Likewise, for bouncing cases, the complainant has to pay a sum of money as a court fee. Further, it varies from case to case. Moreover, it also depends upon the cheque amount that has been bounced. However, the standard court fee structure as the per cheque amount is:
| Cheque Amount | Court Fees |
| ₹0 to 50,000 | ₹200/- |
| ₹50,000 to 2, 00,000 | ₹500/- |
| Above ₹2,00,000 | ₹1000/- |
What Is Relevant Evidence in a Cheque Bounce Case?
For filing against the cheque-bouncing case, the payee must provide relevant evidence to support the case. Moreover, the payee is advised to consult expert lawyers from law firms like Vakilsearch.
The payee, along with the help of their lawyer, has to gather important and useful evidence like the original cheque, cheque return memo, demand notice, and other relevant documents.
Further, they have to provide evidence to support the legal standing of the accused. They are liable to pay an amount with interest as per the amount fit for the mental and physical trauma the payee has to go through during the court hearing process.
What Is the Procedure to File a Civil Suit for a Bounced Cheque?
There are different legal procedures regarding filing the bouncing case. One of the procedures is to file for a civil suit. The drawee can file for a civil suit to recover from the tedious legal battle. The summary suit as per order-37 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, can be used to recover the due amount.
As per order-37 of the code of civil procedure, 1908, the accused in the bouncing case needs to have the permission of the court to defend themselves
Remember, civil suits or summary suits are filed for utilizing them for recovery matters.
How Can a Lawyer Be Helpful Bounced Cheque in India?
Considering the possibilities and provisions under the law, a professional lawyer can be beneficial in a bouncing case. Be it the drawee in the case or the drawer of the case; a qualified lawyer will help you accumulate and manage the paperwork regarding the bouncing case.
Further, they also provide the loopholes present in the cheque-bouncing case. Expert law firms like Vakilsearch will help you guide the entire bouncing case process. A professional lawyer can help the complainant understand the cheque-bouncing case’s legal side.
Further, they can also let the drawee know the legal consequences of the bouncing case. Moreover, they can take their client on the right path before opting for legal suits.
After all, a case like a cheque bouncing can also take up all the energy and time of the client and the accused. So professional lawyers help the client to compromise with the drawee by extending the due date and allowing them to rectify their mistakes.
So, if you happen to face a cheque bounce, consult a qualified and experienced lawyer. This will help the drawee and the complainant to prove themselves.
Cheque Bounce Notice under Section 138
Ever written a check that came back unpaid? It happens! But if the reason is simply not enough money in the account, you can take action. In India, a legal tool called a “cheque bounce notice” can be used in this situation.
This notice is based on Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act. It serves as a formal demand for payment from the person who wrote the check (the drawer) to the person it was written to (the payee).
Here’s the key: The notice is only valid if the check bounced due to insufficient funds. If there’s another reason, like a signature mismatch or a closed account, you’ll need to ask the drawer to reissue the check.
New Cheque Bounce Rule
In August 2021, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced some changes to how cheque bouncing is handled. Here’s the breakdown:
- Maintain a minimum balance: If you rely on checks for payments, make sure you keep enough money in your account to cover them. Bounced checks due to insufficient funds will now result in penalties.
- 24/7 Cheque Clearance: This is good news! The National Automated Clearing House (NACH) now operates around the clock. This means faster cheque processing, including on Sundays.
These changes aim to streamline cheque clearance and reduce bounced checks. By keeping a sufficient balance, you can avoid penalties and ensure your payments go through smoothly.
Circumstances of Cheque Bounce
A bounced cheque can be a frustrating experience. But what causes them? Here are some common culprits:
- Running on fumes: This is the classic case. If there isn’t enough money in your account to cover the cheque amount, it will bounce.
- Time is money: Cheques have a shelf life! If you don’t deposit them within three months of the issue date, they become expired and won’t be processed.
- Second thoughts? Scratching out or changing information on a cheque can make it invalid. Remember, keep it neat and clear!
- Rough ride: Damaged cheques with ripped edges or faded ink can be difficult for banks to read, leading to a bounce.
- Signature slip-up: If your signature on the cheque doesn’t match what the bank has on file, it will be flagged and returned.
- Double check the numbers: Make sure the amount written in words on the cheque matches the numerical amount. Any discrepancy can cause a bounce.
Conclusion
Overall, the court judgment on cheque bounce cases can take up to a year or two. But if the court gets clear primary and relevant evidence to support the case, then the judgment can also happen within a few months. Get in touch with the experts of Vakilsearch to know more.
FAQ’s
What are the steps in a cheque bounce case?
The steps in a cheque bounce case typically involve sending a legal notice, filing a complaint, and presenting evidence before the court.
What is the legal procedure for a bounced cheque?
The legal procedure for a bounced cheque involves sending a legal notice, filing a complaint under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, and presenting evidence before the court.
What is the new rule of a Court Judgment on Cheque Bounce Case?
The new rule of a cheque bounce case is that the offence is punishable by up to two years in prison, a fine equal to twice the value of the check, or both.
What is the punishment for a cheque bounce case?
The punishment for a cheque bounce case can include imprisonment for up to two years, a fine, or both.
Can police take action on a cheque bounce?
Yes, the police can take action on a cheque bounce case, as it is a punishable offence under the Negotiable Instruments Act.
Can I get bail in a cheque bounce case?
Yes, bail is available in cheque bounce cases, but it is subject to the discretion of the court and the specific circumstances of the case.
How do you escape a cheque bounce case?
To escape a cheque bounce case, ensure that you have sufficient funds in your account to cover the amount of the cheque, and respond to any legal notices or court proceedings.
Can I send a cheque bounce notice without a lawyer?
Yes, you can send a cheque bounce notice without a lawyer, but it is advisable to seek legal advice to ensure that the notice is drafted correctly and in accordance with the law.
How can I recover my money from a cheque bounce case?
You can recover your money from a cheque bounce case by filing a complaint under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act and presenting evidence before the court.
What is Defence evidence in a cheque bounce case?
Defence evidence in a cheque bounce case may include any evidence or arguments presented by the accused to challenge the allegations of cheque bounce.
What is the time limit for a 138 case?
The time limit for filing a case under Section 138 of the Negotiable Instruments Act is one month from the date of receiving the memo from the bank about the cheque bounce.
Who pays the penalty for a bounced check?
The issuer of the bounced check is responsible for the penalty on the dishonoured check.
Can a cheque bounce due to bank error be contested?
Yes, a cheque bounce due to a bank error can be contested. If you believe the bank is responsible, gather documents like bank statements and contact them for a reversal. You can also file a complaint with banking authorities.







