Employees’ eligibility for gratuity depends on the last drawn basic salary & many other factors. Read here to know more about gratuity & its eligibility.
Introduction
The non-cash and indirect compensation provided to an employee is known as employee benefits. Employees receive these benefits in addition to their pay and compensation. These benefits, also referred to as fringe benefits, are provided to draw in and retain personnel. Workers highly value benefits and seek recognition for their efforts. One such benefit is gratuity, which employees become eligible for based on their Gratuity Eligibility, determined by the number of years they have served with the company.
Employee and job happiness are directly correlated, and employee commitment will decline if employee happiness is ignored. A company’s most valuable asset is its workforce, and managers should take their employees’ happiness & job satisfaction seriously and increase their investment in employee perks.
According to engagement polls, 50% of workers would quit their jobs in exchange for improved benefits. Benefits are crucial since they raise morale and productivity while reducing absenteeism. For example, if your business can provide employees with medical insurance, they will be less likely to need to take time off for medical reasons. The same is true for student loans, family troubles, parenting concerns, and other factors that affect employees. This article will provide a detailed explanation of what a gratuity is and when an employee is eligible for gratuity India will hold.
An Overview of Gratuity
The Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972 defines gratuity as a reward that may be received. A gratuity is an amount of money given to an employee by their employer in appreciation of work done for the business. However, gratuity is only given to workers who have worked for the company for five or more years. The eligibility for gratuity for an employee can be determined by the services provided by that respective employee to his organisation. It is a component of a worker’s pay and can be considered a retirement assistance benefit plan.
The business must pay a gratuity when an employee leaves a position after working for the same company for at least five years. In 1972, the Payment of Gratuity Act became operative. The terms and conditions you have agreed to with the employer and your most recent salary impact how much gratuity you will get.
An employer may pay gratuities to their staff out of their funds or acquire a group gratuity policy from an insurance company. Typically, the insurance provider covers gratuity in accordance with the group insurance policy, and the employer is required to pay the entire sum.
What is Gratuity in Salary?
Gratuity is a lump sum amount paid by an employer to their employee as a token of appreciation for their services rendered to the company. It is a form of retirement benefit that is paid to employees after a certain period of service. According to the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, salaried employees, excluding temporary or contractual workers, are entitled to gratuity payment after the completion of a certain period of employment at one organization. The gratuity amount depends on the last drawn salary and the number of completed years of service.
For further guidance on navigating the intricacies of gratuity tax exemptions, consider engaging the expertise of Vakilsearch’s professional services. Our knowledgeable professionals are equipped to assist you in making informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
Your gratuity journey, simplified and empowered, awaits!
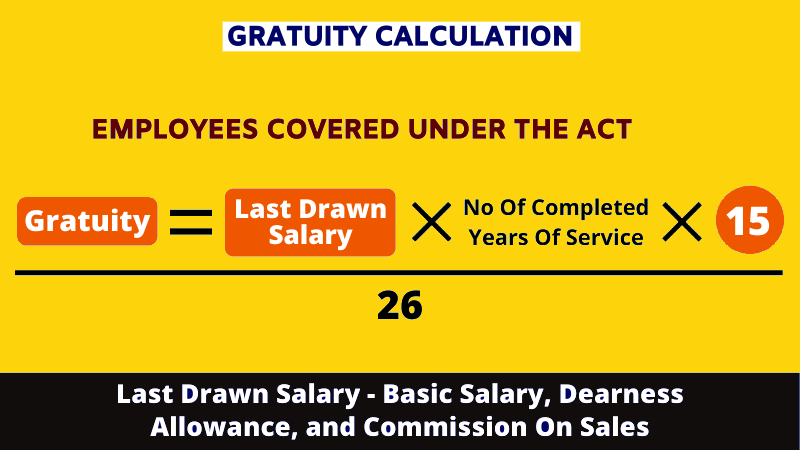
Gratuity Calculation – What is the Formula for Calculating the Gratuity?
Gratuity = n*b*15 / 26
Where n = Tenure of service completed in the company
b = Last drawn basic salary + dearness allowance
In this case, the service years are not rounded off to the nearest integer. The average salary is calculated by taking the average of the basic salary and dearness allowance for the last 10 months preceding the month in which the employee retires or resigns.
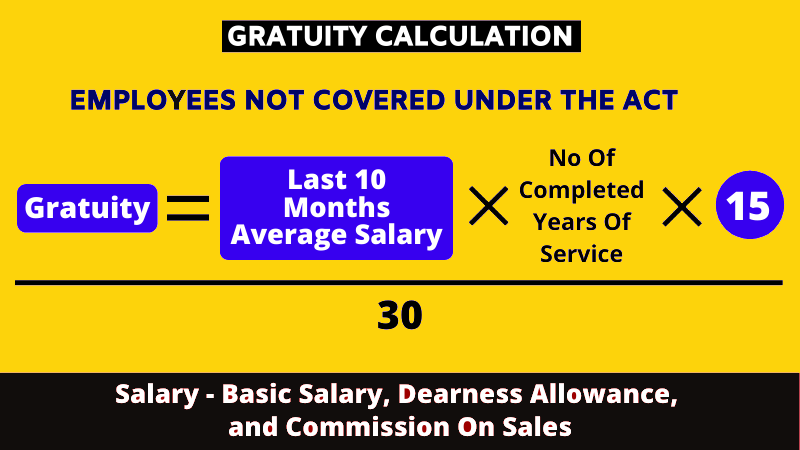
Calculation of Gratuity for the Employees Who Are Not Covered under the Gratuity Act
Even if an organization isn’t covered under the Gratuity Act, it still has the option to provide gratuity to its employees. However, the method of calculating gratuity differs. The calculation is based on half a month’s salary for each year of completed service, encompassing commission (if sales-based), dearness allowance, and basic salary.
The formula for calculating gratuity for employees whose employer is covered under the Gratuity Act is = (15 × last drawn salary × working tenure)/30.
For employees not covered under the Gratuity Act, the total number of days in a month will be considered 30. The calculation of gratuity depends on the last drawn salary (basic salary plus dearness allowance) and the number of completed years of service.
Calculation of Gratuity in Case of Death of an Employee
In the event of an employee’s death, gratuity awards are computed depending on the employee’s length of service. However, the amount is limited to a maximum of Rs.20 lakh. The information below indicates the rates at which a gratuity will be paid in the event of an employee’s death:
Service Duration
Less than a Year: Employees with a service period of less than a year are eligible for gratuity equivalent to 2 times their basic salary.
1 Year or More but Less than 5 Years: Those who have served for a year or more but less than five years are entitled to gratuity equal to 6 times their basic salary.
5 Years or More but Less than 11 Years: For employees with a tenure ranging from five years to less than eleven years, the gratuity amount stands at 12 times the basic salary.
11 Years or More but Less than 20 Years: Individuals who have dedicated their service for eleven years or more but less than twenty years are eligible for gratuity equivalent to 20 times their basic salary.
20 Years or More: Those with a commendable service duration of twenty years or more receive gratuity that’s half of their basic salary for every completed six-month period. Importantly, this is subject to a maximum cap of 33 times the basic salary.
Latest Advancements in Regard to Gratuity
The Centre recently in an amendment raised the maximum gratuity limit. It is now tax exempt up to Rs 20 lakh, up from the previous limit of Rs 10 lakh under Section 10(10) of the Income Tax Act. The CBDT Notification No. S.O. 1213(E), issued 8 March 2019, specified that the Rs 20 lakh exemption limit would apply to employees who retired, died, resigned, or became disabled on or after March 29, 2018.
Few Significant Points About Gratuity
- An employee is eligible to receive a gratuity amount after completing five years of continuous service at one organization.
- The gratuity amount is paid to the employees once they retire, pass away, resign, or are laid off.
- The gratuity amount earned by an employee depends upon the tenure of the service and the last drawn salary.
- If an employee receives gratuity during their tenure, then it is fully taxable as income in their hands.
- If gratuity is received in case of an employee’s resignation or death and some other cases, then tax exemption is applicable under section 10(10) of the Act.
- Certain organizations are entitled to gratuity as prescribed in the 1972 Payment of Gratuity Act.
Tax on Gratuity
Taxation on gratuity hinges on the recipient’s employment status and the nature of their employer. The calculation of tax on gratuity primarily revolves around two scenarios:
Government Employee Receiving Gratuity Amount:
If the gratuity is received by an employee under the state government, central government, or local authority, the entire gratuity amount is exempt from Income Tax.
Salaried Individual Receiving Gratuity Amount from a Gratuity Act-Covered Employer:
For employees receiving gratuity from employers covered by the Gratuity Act, tax exemptions apply based on the following:
- 15 days of last drawn salary for each completed year of service
- The gratuity amount actually received by the employee
Salaried Individual Receiving Gratuity Amount from a Non-Gratuity Act-Covered Employer:
When the employer is not covered by the Gratuity Act, the following conditions determine tax exemptions:
The lowest of the three: Rs.20 lakh, actual gratuity received, or eligible gratuity amount.
Tax Exemptions on Gratuity
In light of the 2016 budget amendments, the landscape of gratuity laws has undergone notable revisions. Here’s an overview of the modifications and how they shape the current gratuity tax exemptions:
As per Article 10 (10) within the Income Tax Act, gratuity received by government employees, excluding statutory corporations, enjoys complete tax exemption.
Article 10 (10) ii of the Income Tax Act outlines tax exemption criteria for death and retirement gratuity for employees covered by the Gratuity Act of 1972. The exempted amount is determined based on the lower value of the following:
- (15/26) multiplied by the Last Drawn Salary* and then multiplied by completed years of service or any part thereof exceeding 6 months.
- Rs. 20 lakh.
- The actual received gratuity sum.
*In the case of an individual employed in a seasonal establishment, the calculation is based on 7 days.
**The term “Salary” encompasses the aggregate salary received by an employee, encompassing Dearness Allowance. It excludes additional benefits like HRA, bonus, commission, and other perquisites.
Article 10 (10) iii of the Income Tax Act addresses gratuity exemptions for individuals not covered by the Gratuity Act of 1974. The exemptions are as follows:
- Half Month’s Average Salary* multiplied by completed years of service.
- Rs. 10 lakhs.
- The actual received gratuity amount.
*Average salary is computed by taking the average of the salary over the last 10 months directly preceding the retirement month. **Salary consists of Basic Pay, Dearness Allowance (to the extent it contributes to retirement benefits), and commission based on turnover.
Advantages of using a Gratuity Calculator
Here are the numerous advantages of using a gratuity calculator –
- Using a gratuity calculator can help calculate the gratuity amount based on the formula for calculating the gratuity.
- A gratuity calculator can be used from the comfort of your home or practically anywhere to get the gratuity figure in seconds.
- It saves time and effort and provides an accurate estimate of the gratuity amount.
- The calculator takes into account the last drawn salary and the number of completed years of service to calculate the gratuity amount.
Gratuity Rules
To make sure the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972’s laws and regulations are followed, the Indian government undertakes the following inspections that makes employees eligible for Gratuity
- It scrutinises the establishment to see if it has registration under the act’s guidelines. You must register with the relevant Assistant Commissioner of Labour.
- Second, it looks to see if the employer gave the governing authority notice of the case’s opening, modification, or closure.
- Thirdly, it checks to see if an abstract of the Act and its regulations is visible.
- Additionally, it verifies that the employee has approved of their nominations.
- It also verifies if the controlling authority received a copy of the notice outlining the admissibility or non-admissibility of the gratuity claim.
- It also makes sure that everyone is aware of any fatalities or accidents in the preceding year.
- Additionally, it examines and confirms the specifics of any legal infractions.
Gratuity Eligibility Criteria For Employees
An employee eligible for gratuity payment can be determined through a number of circumstances. Following are a few of them:
- When the worker qualifies for pension or superannuation benefits.
- When an employee departs from a company after five years of service.
- Upon retirement the worker.
- Any abrupt impairment brought on by a mishap or a serious disease suffered by the employee.
- Upon the employee’s passing.
The employee’s nominee receives the gratuity payment in the event of their death. Their heirs will be the nominee. The paying sum is put in a bank or other financial institution with the governing authority if the heir is a minor. The controlling authority will subsequently invest the payment for the benefit of the minor. This will hold true up until the successor qualifies as a major. If a male employee passes away, his family will be regarded as their nominee. The nominee may be his or her spouse, children, parents who are dependent on him or her, etc.
Similar to this, if the worker is a woman, her family will consist of her spouse, kids, dependent in-laws, dependent parents, etc. The child will also be regarded as a family member if the employee has formally adopted the youngster. The employee’s child, however, will not be regarded as a family member if a different person has acquired that child.
Gratuity Calculation
-
Employees Covered Under the Act
-
Employees Not Covered Under the Act
Conclusion
The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 provides immense benefits for employees. An employee may, by the statute, designate a family member for gratuity and other benefits when they join your organisation. This will make it possible for the family member to receive the money even after the employee has passed away. Even though the business is losing money, the corporation is still required by the statute to pay the employee’s due gratuity. The highest gratuity paid by the employer is ₹10 lakhs. This enables many employees to get high tip payments. The corporation may contribute more than ₹10 lakhs, but it won’t be taken into account for tax exemption purposes anymore. Even if the employer files for bankruptcy, every employee is entitled to a gratuity. If the employee is eligible for Gratuity benefits, no court may withhold the gratuity due to them.
All employees should endeavor to accept their gratuities from the companies they have devoted their time and effort to build a reasonable corpus for their future. For your business to attract and retain top talent, it’s critical to offer the correct incentives and bonuses to employee Alsoally; it contributes to a diverse workplace. Understanding your employees’ needs and interests is another strategy.
FAQs on Gratuity Eligibility
Is 4 years 7 months eligible for gratuity?
In the Salem textile case (2011), the Madras High Court ruled that an employee is entitled to a gratuity even if he has worked for four years and 240 days. To understand whether or not the same rule applies in your jurisdiction, get in touch with our experts right away.
Who is eligible for gratuity salary?
Employees covered under The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 are eligible for gratuity salary provided they fulfil the minimum conditions prescribed under the Act.
Is 4 years 8 months eligible for gratuity?
The Madras High Court has ruled that an employee is entitled to a gratuity even if he has worked for four years and 240 days. To understand whether or not the same rule applies in your jurisdiction, get in touch with our experts right away.
What is gratuity new rules 2023?
According to Gratuity new rules 2023 - Employers must ensure that base pay accounts for 50% of an employee's CTC (cost to the company) and that the remaining 50% is made up of overtime, housing costs, and employee allowances under the new gratuity policy for 2023. Furthermore, any additional allowances or exemptions paid by the employer that exceed 50% of the CTC will be considered payment.