Learn the complete trademark registration process in india with Vakilsearch. Check how to register a trademark in India, process, fees, classes, and benefits.
The trademark registration process ensures the legal protection of your intellectual property. By filing a trademark application with the Trademark Office, businesses secure exclusive rights to use their unique signs to identify goods or services. A registered trademark helps differentiate products from the competition, prevents infringement, and provides significant legal benefits. Trademark protection is governed by the Trademark Act, 1999, which safeguards these rights.
When applying for trademark registration, the applicant must submit Form TM-A and select the appropriate trademark class for their goods or services. The process includes examination, potential opposition, and publication in the Trademark Journal. Once registered, a certificate of registration is issued, enhancing brand recognition and brand value. A logo is a common example of a trademark that helps to establish a strong identity in the market.
The trademark fees vary depending on the filing method. Online filing (e-filing) is more affordable, while offline filing may incur additional charges. Understanding the fees and application timeline ensures a smooth process. The trademark status will indicate whether the application is pending, rejected, or successfully registered. Trademarks are initially valid for 10 years from the registration date and can be renewed indefinitely every 10 years to maintain their protection under the Trademark Act.
What is a Trademark and Why Should You Register a Trademark?
A trademark is a unique symbol, word, phrase, or design used to identify a specific product or service and distinguish it from others. As an essential form of intellectual property, it helps businesses protect their brand and maintain a unique identity in the market.
In India, trademark registration is regulated under the Trade Marks Act, 1999. While it is voluntary, registering a trademark is vital for businesses to protect their brand identity and differentiate their goods or services. A registered trademark helps build trust and goodwill with customers, reinforcing the brand’s reputation and ensuring that the business’s offerings are seen as unique and high quality.
Trademark registration grants exclusive rights to the owner, safeguarding against infringement and unauthorized use of similar trademarks that could confuse consumers. It provides legal protection, ensuring the business maintains control over its intellectual property. Registering a trademark is a key step for businesses aiming to strengthen their market presence and secure their brand for long-term growth.
Who Can Apply for a Trademark?
In India, any individual, company, LLP, partnership firm, or legal entity engaged in trade or commerce can apply for trademark registration, as long as they meet the eligibility criteria for trademark registration. Successful registration grants the applicant exclusive rights to use the trademark for the specified goods or services.
- An individual
- Joint owners
- Proprietorship firm
- Partnership firm
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- Indian company
- Foreign company
- Trust or society
Trademark Registration Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The trademark registration process in India follows a structured series of steps governed by the Trademark Act, 1999. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages:
Step 1: Trademark Search
Before filing, a trademark search is essential to check for identical or similar trademarks. This search helps avoid potential conflicts with existing marks. You can conduct the search via the Trademark Registrar’s website or through a trademark agent.
Step 2: Filing a Trademark Application
Once the trademark search is complete, file the trademark registration application with the Trademark Registrar, either online or at the relevant office. The application must include details like the logo, applicant’s information, trademark class, and the fee for registration.
Step 3: Trademark Application Allotment
After filing the application, the Trademark Registrar assigns a unique application number within a couple of working days. You can track the application status online. The TM symbol can be used once the allotment number is issued.
Step 4: Vienna Codification
The Vienna Codification classifies figurative elements of marks. If the trademark includes logos or designs, the Trademark Registrar applies this classification. The status will reflect as “Sent for Vienna Codification” during this phase of the trademark registration process.
Step 5: Trademark Fees Payment
The prescribed government fees must be paid depending on the type of applicant and number of classes under which protection is sought.
Step 6: Trademark Examination
Once Vienna Codification is completed, the application is reviewed by a Trademark Officer for correctness. The officer may accept the application or issue objections. If there are objections, the applicant can present justifications before the officer for approval.
Step 7: Trademark Objection
If any trademark objection is raised, the applicant must respond with clarification or evidence within a stipulated period to avoid abandonment.
Step 8: Trademark Journal Publication
After acceptance, the trademark is published in the Trademark Journal, allowing the public 90 days to file objections. If no objections arise within this period, the trademark is typically registered within a few months, following due publication procedures.
Step 9: Trademark Opposition
If a third party files an opposition within the 90-day period, a hearing is scheduled. Both the applicant and the opposing party present their arguments, and the Trademark Hearing Officer decides based on the evidence whether the trademark should be granted.
Step 10: Hearing on Trademark Opposition
If an opposition is filed, a trademark hearing is held to decide the matter based on submissions and evidence from both parties.
Step 11: Trademark Registration Certificate
Once no objections are filed, and the opposition process is resolved, the Trademark Registrar issues the trademark registration certificate, granting exclusive use of the trademark. The ® symbol can now be used, officially marking the trademark as registered.
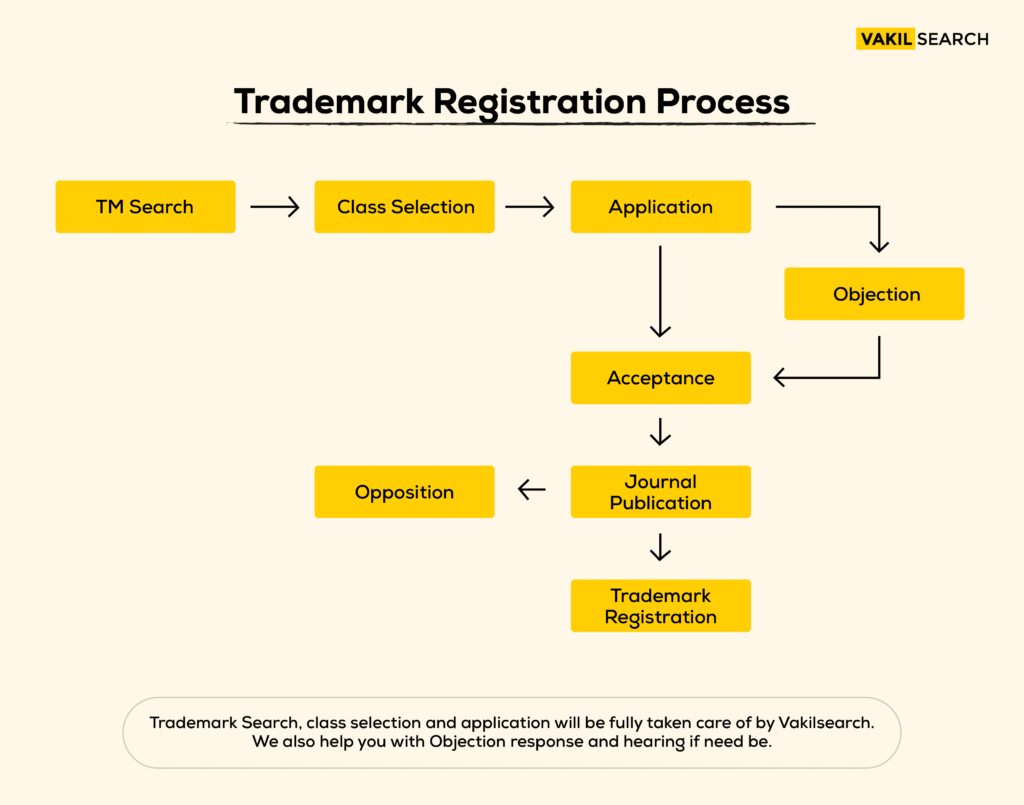
Trademark Registration Process Flowchart
Understanding the trademark registration process is crucial for avoiding legal complications. A trademark registration flowchart simplifies the steps, guiding you through trademark searches and key trademark characteristics. This provides clear stepwise navigation for an effective trademark application.
Trademark Registration Fees
Trademark registration fees in India vary based on the type of applicant and the number of classes under which the goods or services are categorized. The fees are structured as follows:
- Individual/Startups/Small Enterprises:
-
-
- For one class: ₹4,500
- For multiple classes: ₹4,500 per class
-
- Other Entities (Companies, LLPs, Trusts, etc.):
-
-
- For one class: ₹9,000
- For multiple classes: ₹9,000 per class
-
Additional Details:
-
- The fees are non-refundable once the application is submitted, regardless of whether the application is approved or rejected.
- Payment can be made online through the official Trademark Registry portal or via offline methods at the respective office.
How to Check the Status of a Trademark Application
After filing a trademark application, the Trademark Registry assigns an allotment number, which serves as a unique reference to track the status of the application. You can use this number to check trademark status on the official IP India Trademark Status portal. The application goes through various stages—formalities check, examination, publication in the journal, opposition (if any), and finally, registration or refusal.
Typically, it may take 6 to 18 months to receive approval or rejection, depending on objections, oppositions, or document clarifications. Factors like similar existing marks, incomplete documentation, or opposition by third parties can cause delays. Applications from startups or small enterprises often receive priority processing if opted for.
Importantly, you can start using the ™ (TM) symbol immediately after filing the application to indicate a pending trademark. However, you may use the ® (registered) symbol only after official registration is granted by the authority.
Trademark Renewal, Expiry & Rectification
A registered trademark in India is valid for 10 years from the date of registration and can be renewed indefinitely for additional 10-year periods. The trademark renewal process should ideally begin within six months before the expiry date to avoid lapse. Renewal ensures continued legal protection and exclusive rights over the trademark.
If a trademark is not renewed, it expires and is removed from the Trademark Register. However, the owner may apply for restoration within one year of expiry by paying a late fee along with the renewal fee. In cases where incorrect or misleading entries are made in the Trademark Register, trademark rectification can be requested by the registered owner or an aggrieved party. This legal process allows correction, cancellation, or modification of the trademark record, ensuring that the registry reflects accurate and updated information.
Benefits of Trademark Registration in India
Registering a trademark offers several benefits of trademark registration, such as exclusive usage rights, brand protection, and the ability to build goodwill. It helps differentiate products, ensures quality, and provides long-term legal security for your brand.
Exclusive Usage Rights
Trademark registration grants the owner exclusive rights to use the mark for the goods or services it represents. This ensures that no other entity can use an identical or deceptively similar mark, providing a legal monopoly over the brand identity. It helps build a strong market position and prevents brand dilution.
Builds Goodwill
A registered trademark symbolizes a brand’s reputation and trust built over time. It reflects consistency, reliability, and quality, which boosts customer confidence. Over time, this goodwill increases the brand’s value, making it easier to retain loyal customers and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Differentiates Products and Services
Trademarks help consumers distinguish one brand’s products or services from another. It creates a unique identity that separates a business from its competitors. This distinction is crucial in markets where similar products are offered, making it easier for customers to identify and choose your brand.
Ensures Product Quality
A trademark serves as a symbol of consistent quality. When customers recognize a brand through its trademark, they associate it with specific standards. This encourages businesses to maintain or improve their quality to preserve their brand’s reputation and customer satisfaction, ultimately boosting long-term loyalty.
Helps in the Creation of an Asset
Registered trademarks are intangible assets that can appreciate in value. They can be sold, licensed, or franchised, making them a powerful business tool. As the business grows, the value of the trademark increases, contributing to the overall financial worth of the company.
Usage of Ⓡ Symbol
Once registered, a brand can legally use the Ⓡ symbol to indicate official ownership of the trademark. This symbol serves as a public notice of your rights and deters potential infringers. It also adds credibility and authenticity to the brand, reinforcing trust among customers.
Protection Against Infringement
Trademark registration provides legal protection against unauthorised use, imitation, or duplication of your brand. If infringement occurs, the owner has the right to take legal action and claim damages. This helps safeguard the brand’s identity and ensures fair market practices.
Protection For Ten Years
A registered trademark is valid for a period of 10 years from the date of application. It can be renewed indefinitely every decade. This long-term protection ensures sustained brand security and legal exclusivity, allowing businesses to plan their growth without fearing identity theft.
Global Trademark Registration
Indian trademark registration can serve as the basis for international registration under the Madrid Protocol. This allows businesses to expand globally and secure trademark rights in multiple countries. It’s an essential step for companies aiming to build a global brand presence.
Attract Customers
A strong, recognizable trademark draws attention and fosters consumer trust. Customers are more likely to buy from a brand they recognize and trust, giving the business a significant edge. A trademark acts as a marketing tool, driving brand loyalty and enhancing visibility in competitive markets.
FAQs on Trademark Registration Process
What are the steps for trademark registration?
The trademark registration process involves conducting a trademark search to ensure uniqueness, filing an application with Form TM-A, paying the fee, undergoing examination, addressing objections, and, if successful, receiving a certificate of registration for legal protection.
How much does it cost to register a trademark?
The cost of trademark registration in India ranges from ₹4,500 to ₹9,000. Individuals, startups, and small businesses can avail the lower fee of ₹4,500, while companies or LLPs pay ₹9,000 for each class during registration.
How to get a TM certificate?
- Step 1: Go to the official Trade Marks Registry website.
- Step 2: Click on 'Trade Mark Application/Registered Mark.'
- Step 3: Select 'National/IRDI Number' option.
- Step 4: Enter your trademark application number and captcha code.
- Step 5: Click 'View' to display the trademark details.
- Step 6: Select the trademark number.
- Step 7: Click on 'View Registration Certificate.' and download the trademark certificate as a PDF.
How much time does it take to get a trademark registered?
Trademark registration typically takes 18-24 months if there are no objections or oppositions. The application number is issued within 1-2 days, but the overall process may be quicker if the application is filed correctly without issues.
Can I apply for a trademark myself?
Yes, individuals in India can apply for trademark registration themselves. If you are the owner of a trademark, you may file the application under the relevant trademark laws without requiring a trademark agent or lawyer.
How do I check my trademark status?
To check your trademark status, visit the IP India website, select 'Trade Mark Application/Registered Mark,' and click on 'National IRDI Number.' Enter the trademark application number and captcha, then click 'View' to see the status.






