Getting separated from one’s parents legally for a minor is crucial in cases of abuse. The Emancipation process may be life-saving for many children. Learn how to separate from parents legally in less than 5 minutes and avoid abuse.
In India, the legal framework surrounding separation from parents is complex and nuanced. It’s crucial to understand the key points before making any decisions. Here’s an overview:
General Principles
- Age: The legal framework differs based on your age. Minors (below 18) and adults (18 and above) have different options and limitations.
- Parental Responsibility: Parents have a legal duty to care for and protect their children until they reach adulthood.
- Right to Life and Personal Liberty: This fundamental right, enshrined in the Indian Constitution, allows individuals to choose their lives, including where they live and whom they associate with.
Options for Separation
-
For Minors (Below 18)
- Emancipation is a legal process where a minor is declared an adult and freed from parental control. It requires substantial evidence of a dysfunctional family environment, financial independence, and the ability to manage adult responsibilities.
- Child Protection Measures: In cases of abuse, neglect, or exploitation, a minor can seek protection through Child Welfare Committees or the Juvenile Justice System.
-
For Adults (18 and Above)
- Financial Independence: Establishing financial independence empowers individuals to live on their own and make independent decisions.
- Moving Out: Adults can leave their parents’ homes and live independently without legal repercussions.
- Limited Parental Control: Parents’ control over adult children is limited after they turn 18. However, they may still have certain rights regarding inheritance and property.
Eligibility Criteria for Legal Separation from Parents
Emancipation grants an adult status to the child by or before the age of 18 through a legally binding process. The judge orders the child to be freed from the care and custody of their parents or legal guardians.
A child can apply for emancipation if,
- The parents are abusive and they can’t take care of the child
- The situation in the parent’s home is emotionally, morally, and physically harming
- The child has reached financial independence and wants adult rights
- The applicant is a major and prefers to stay alone.
Steps to File a Legal Separation from Parents
The court takes emancipation very seriously and therefore sets greater standards for reviewing or granting the petition. Emancipation is applied to different scenarios. In some cases, the minors seek emancipation because they are already independent or living on their own but find it difficult to rent an apartment or enter into contracts as underage minors. Others are in a critical or life-threatening situation at home. In such cases, children opt to run away from home. Instead, they can apply for the emancipation procedure. The emancipation process varies from state to state.
- Initially, the state court demanded a petition to be submitted stating why you wish to separate from the parent
- Then you must inform your parents in writing regarding the will to separate. You will be notified of the date and time of the hearing
- Now the judge will decide regarding the approval of your request for the release
- It is usually better to write a declaration of intent to explain the present situation in your life, why you want to be legally separated from your parents, and how you intend to make a living
- The applicant can also include letters of recommendation from a concerned person like the applicant’s employer, teacher, or landlord
- The process becomes very easy if the parents sign a declaration of emancipation for minors. But if you are not aware of their whereabouts you stand liable to inform the court
- The process becomes complicated if parents refuse to sign the consent form. In this case, they will receive a hearing notice from the court via mail.
A copy of all the materials including proof of income and other documents should be provided. In general, judges do not permit separation unless there is enough proof of financial stability. The applicant should attach the bank statement, salary, and credit card information if any.
Costs Involved in Filing a Legal Separation from Parents
Go to court: https://districts.ecourts.gov.in/ and pay the fee to apply for separation. This is usually pretty low. However, this does not involve the prices of a personal lawyer. If you cannot afford to pay the fee, you can get a fee exemption by appealing to the public prosecutor or other charitable law firms. You cannot start the separation process without a fee or exemption.
Court’s Point of View in Filing a Legal Separation from Parents
The legal bodies don’t stop anyone from separating from their parents and instead demand proof that the minors seeking emancipation are ready for adult responsibilities. As a part of this process, they may verify that the applicant is currently employed can afford secure housing, and have an overall awareness of how to manage other aspects of life. Know about Divorce Alimony online.
It’s not ideal to expect public aid after emancipation. In that case, the court may decide to involve a state`s child welfare agency if your parents are considered unfit as guardians.
Exceptions in Filing a Legal Separation from Parents
As per the rules and regulations, people with mental disabilities and those who are differently-abled in a way that they are incapable of caring for themselves will not be considered or legally viewed as emancipated, despite reaching an age of maturity. The non-emancipated status will not affect any other legal aspects.
Legal Considerations and Implications
When a child in India decides to separate from their parents, it brings forth a range of legal considerations and implications. The law prioritizes the child’s well-being while navigating this complex situation, which involves assessing the child’s ability to make independent decisions, family dynamics, and the evolving nature of parent-child relationships.
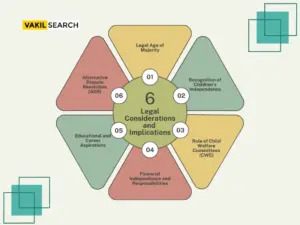
-
Legal Age of Majority:
In India, reaching the age of eighteen signifies legal adulthood and the ability to make independent decisions, including choices about living arrangements. Courts intervene only when there are significant concerns for the child’s welfare and independence.
-
Recognition of Children’s Independence:
There is a growing legal recognition in India of older children’s autonomy, especially in cases of voluntary separation where the child’s wishes are taken seriously if deemed capable of making informed decisions by the court.
-
Role of Child Welfare Committees (CWC):
Child Welfare Committees play a crucial role in assessing situations involving voluntary separation, focusing on the child’s well-being. The voluntary nature of the decision is pivotal in safeguarding the child’s interests.
-
Financial Independence and Responsibilities:
Financial considerations arise when a child seeks legal separation from parents. Courts evaluate the child’s ability to support themselves, yet parents typically remain responsible for their support until adulthood.
-
Educational and Career Aspirations:
Courts also consider the child’s educational and career goals when assessing the situation, prioritizing decisions that align with the child’s best interests.
-
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR):
Utilizing methods like mediation can facilitate constructive dialogue and agreements that satisfy both parties, promoting a more amicable resolution while keeping the child’s well-being at the forefront.
How Vakilsearch Can Help in Filing a Legal Separation from Parents
The legal separation of a child from a parent is complicated. You must follow the timeline set by the court to submit the appropriate documents, notify your parents of your intention to leave them, and appear in front of the judge for a hearing.
Due to this complexity, legal advice is mandatory. Vakilsearch can bring great benefits in helping to structure the process and achieve the best results. Reach out to the experts at Vakilsearch for complete legal assistance.
FAQs
Is separation a legal status in India?
No, separation is not legally recognized in India. There are legal processes like emancipation for minors and independent living for adults that lead to factual separation, but these don't constitute a formal legal separation status like in marriage.
What is the difference between legally separated and divorced?
Divorce refers to the legal dissolution of a marriage, severing all legal ties between spouses. Separation, however, applies to parents and doesn't dissolve any legal ties. It generally involves living independently and making separate decisions, but parental rights and responsibilities towards children often remain in place.
How can I separate from my parents in India?
The options for separation depend on your age:
Minor (Below 18): You can seek emancipation through court based on specific circumstances like abuse, neglect, or financial independence. Alternatively, you can seek protection through child welfare mechanisms if facing harm.
Adult (18 and Above): You can establish financial independence and move out to live independently. The law grants you the right to make such decisions without legal repercussions.
What not to do during separation?
Refrain from acting impulsively or making hasty decisions. Open communication with your parents might resolve some issues and avoid legal complexities.
Do not engage in illegal activities or neglect your responsibilities towards family and obligations.
Do not disregard any legal advice or court orders you might receive during the process.
How can I prove separation in India?
Proof of separation can be crucial in specific situations like child custody matters. Evidence like independent residency, separate financial records, and witness statements can help establish separation, but always consult a lawyer for specific guidance.
What are the three types of separation?
The term 3 types of separation isn't directly applicable to parent-child separation in India. However, different mechanisms like a judicial separation (for spouses), legal separation through agreements (for couples), and de facto separation (living apart) exist in other contexts.
Is legal separation valid in India?
As mentioned earlier, a legal separation doesn't exist as a distinct legal status for parents in India. The options involve either achieving independence as an adult or seeking legal intervention like emancipation for minors through the courts.




