Learn about the various trademark status options, including pending, approved, refused, cancelled, and abandoned, and understand the significance of each in the trademark registration process. Stay informed and protect your brand's identity.
Let’s see a bit about trademark and the process to register a trademark before we move on to see how to check trademark status. A trademark is a kind of recognisable expression, word, symbol or sound that denotes a certain product and thereby differentiates it from all the other products in the request. It’s a commodity that recognises the ownership of the brand.
Process of Registering a Trademark
An application must be submitted in the form TM- A to the Trademarks Registry in order to register that particular trademark. The prescribed fee must also be paid. It’s always judicious to keep tab on the trademark status because there are cases when the aspirant may have to act upon the same to make sure that the trademark gets registered soon.
How to Check Trademark Status in India?
- Step 1: Visit the official site of the government for trademark applications: https://ipindiaonline.gov.in/eregister/eregister.aspx to register.

- Step 2: On the left-hand side of the screen, pick the first option, ‘Trade Mark Application/Registered Mark.’ Two options are available there. Click on the National IRDI Number.
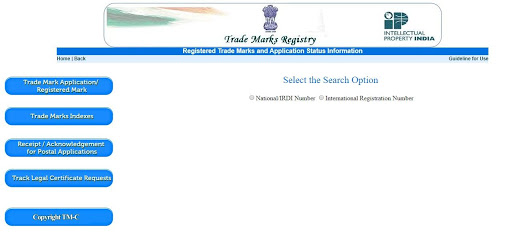
- Step 3: You must provide the trademark application number. And enter the captcha code. After you’ve entered all of your information, click ‘View’.

Further, the website will show you the status of your application.
Trademark Status –Types
It is critical to comprehend what each sort of status means in regard to the application in order to choose the appropriate course of action in the case of a new programme.
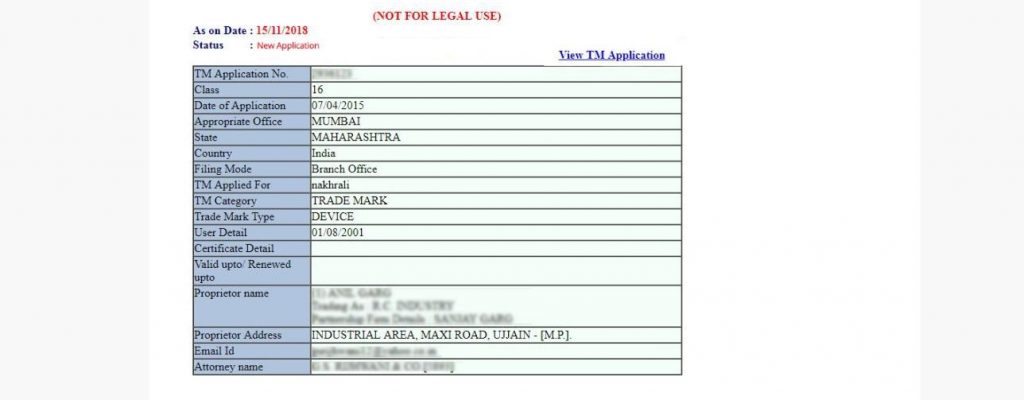
1. New Application
The status ‘New Application’ indicates that the application has recently been received for further review. This stage signifies the beginning of the application process. Additionally, it has yet to be thoroughly examined.
2. Sent to the Vienna Codification
The Vienna Code Classification is a globally recognised standard for logos and their components. Similarly, the Code is determined by the nature of the logo’s figurative parts.
You can locate previously registered trademarks to prevent copyright infringement using the Trademark Search tool at Vakilsearch.
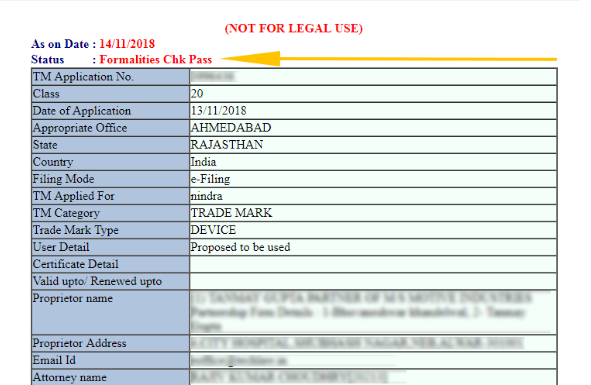
3. Formalities Check Pass
The Trademark Registry accepts all of the initial/preliminary materials provided with the application at this stage of the trademark. In other words, there are no issues with the documents that have been presented thus far.
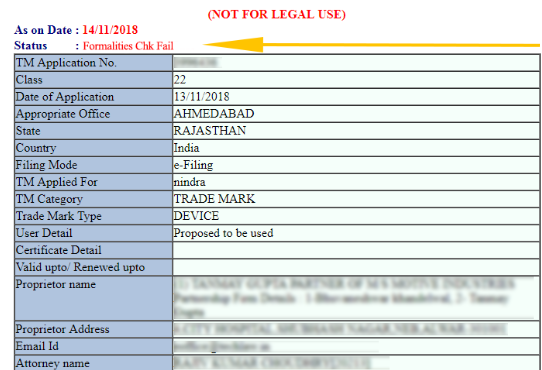
4. Formalities Check to Fail
The status while checking the will be interpreted as ‘Formalities Check Fail’ if the Trademark Registry detects any flaws or discrepancies with the papers that were initially supplied with the application by the applicant.
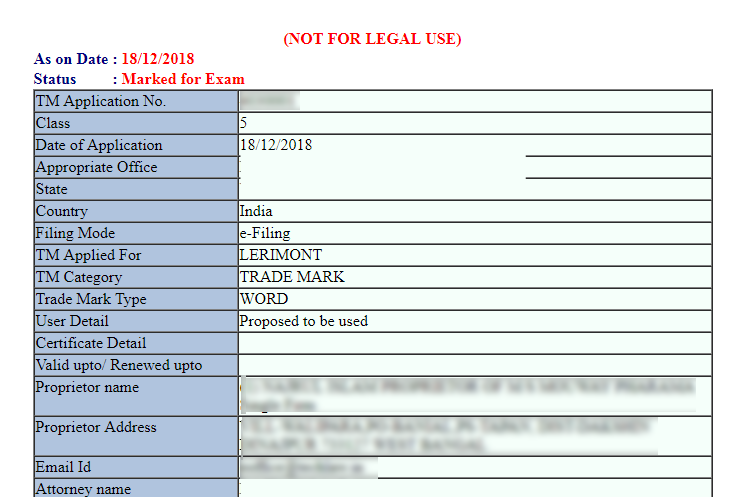
5. Marked for Exam
If the trademark obtains a ‘Formalities Check Pass’ after an initial round of checks, it will be submitted to a Trademark Examiner, who will examine all of the papers as well as the application to verify it is complete in all respects.
6. Objected
It signifies that the examiner has expressed some concerns about the trademark and its registration. Moreover, the examination report must be responded to within a month of its issue in this circumstance, barring which, the trademark status will be changed to ‘Refused.’
7. Refused or Abandoned
The examiner will stamp the application as ‘Refused or Abandoned’ if he is not satisfied with the response to the Examination Report or even after a Show Cause Hearing.
8. Advertised Before Accepted
In some circumstances, the trademark status displays ‘Advertised before Accepted.’ Likewise, this indicates that the Trademark Registrar is still undecided regarding the trademark’s nature.
9. Accepted and Advertised
The Trademark Registrar is happy with the character of the trademark at this point and hence authorizes it to be registered in the Trademark Journal since it is unique enough to be recognised as a trademark.
10. Opposed
The general public has 3-4 months after the trademark is announced and published in the Trademark Journal to reply in terms of trademark opposition. Further, any opposition filed after the time limit has expired will be ignored. During that period the status is reflected as ‘opposed’
11. Withdrawn
The applicant might opt to contest the opposition case if the trademark status is ‘Opposed.’ Likewise, if the applicant decides not to pursue the lawsuit, he or she might withdraw the trademark application voluntarily. Therefore, the trademark’s status will be ‘Withdrawn.’
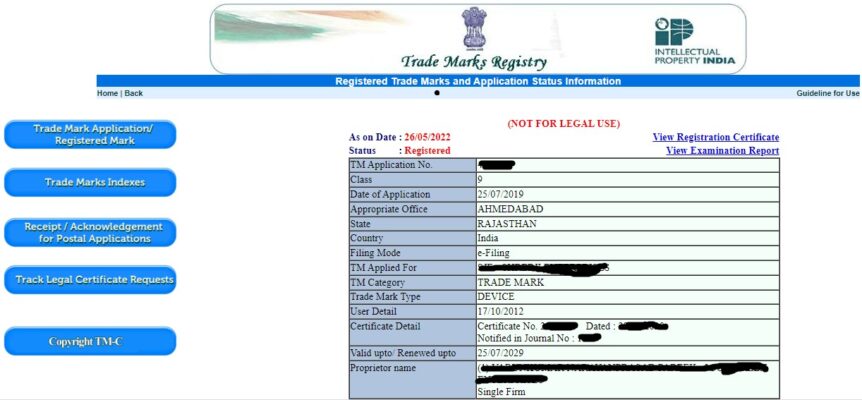
12. Registered
The Trademarks Registry issues a certificate of registration to the applicant against his or her application once the trademark application has been approved through the ‘Accepted and Advertised’ stage. At the same time, the status on the webpage is updated.
13. Removed
The trademark can be withdrawn from the Trademark Journal if it has not been used for five years following the issuing of the Trademark Registration Certificate, or if the trademark owner forgets to renew the trademark registration. ‘Removed’ should be the status at this time.
Thus, it’s always judicious to take out time and give clear documents inorder to avoid any kind of detention with regard to the enrollment of the trademark.
FAQs on Trademark Status
How can I check the status of my trademark application?
To check your trademark status, visit the Trademark Status Website at https://tmrsearch.ipindia.gov.in/eregister/eregister.aspx. Navigate to the Trademarks Tab, click on the Related Links Section, and select Trademark Status. Then, enter your trademark application number along with the Captcha code and select ‘View’ to see the trademark status. You’ll be able to check the Trademark Number, Trademark Filing Date, and the National IRDI Number for your Intellectual Property (IP).
How can I check if a trademark is registered?
Step 1: Go to the Vakilsearch Trademark Search Page. Step 2: Type your desired brand name in the search field and click 'Search Trademark'. Step 3: The results will show the trademark status, such as whether it is registered, abandoned, or has other related status. Step 4: The results will also display the trademark application number, date, proprietor name, and trademark type. Step 5: If your trademark is unavailable, connect with Vakilsearch trademark experts for guidance on trademark registration.
What is the legal status of trademark?
The legal status of a trademark provides legal protection to the trademark owner. If there’s misuse, the owner can contest it in a court of law. You can use the TM symbol after filing the trademark application.
What happens after the formalities check pass in trademark?
When the trademark application status shows 'Formalities Chk Pass', it means the necessary documents and information have been submitted correctly. However, this status does not mean the trademark has been registered yet.
What does it mean when a trademark is pending?
A trademark application that is pending indicates that the USPTO has received it but has not yet approved it. The application typically takes 8 to 10 months to process. Trademark rights are retroactive to the filing date, and refusals may occur if forms are inaccurate or incomplete.
What is published status in trademark?
Published status in trademark means the mark has been accepted and published in the TM Journal. If no opposition is filed within four months, the trademark becomes eligible for registration, and the certificate is issued through the automated TM system.
What is Marked for Exam status in Trademark?
The 'Marked for Exam' status means that the trademark application is under review by a trademark examiner for an examination report. This process typically takes 1-3 months, after which the trademark officer will generate the report, indicating whether the application is accepted or objected to.
What is refused status in trademark?
The 'refused' status means that the trademark application has been denied and will not proceed to registration. This status is updated on the IP India website after the trademark examination reveals issues.
What is objected status in trademark?
Objected status means the Trademark Office has raised objections to your trademark application in the examination report. Either the registrar or examiner can file the objection. You must reply to the objection within one month to continue the trademark registration process.