Discover the latest GST exemptions in 2025! Learn about exempted goods, services, turnover limits, and their impact on businesses and consumers.
GST Exemptions play a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape by supporting sectors critical to societal welfare and development. In 2025, the GST policy continues to exempt a broad array of goods and services, ensuring affordability and accessibility for essential commodities. Products like fresh agricultural produce, medical supplies, and educational materials are kept outside the GST ambit to reduce the financial burden on consumers.
The exemption policy extends to vital services, covering sectors such as healthcare, education, and charitable activities. By excluding these services from GST, the government aims to promote social welfare and enable organizations to provide necessary services without the additional tax overhead. This strategic approach helps maintain the accessibility and affordability of crucial services that contribute significantly to public well-being.
Additionally, GST exemptions are designed to support small businesses and startups by establishing clear turnover-based exemption thresholds. This framework encourages business growth and economic participation without the complexities of tax compliance. The exemptions not only simplify the business operations but also aid in fostering a conducive environment for new ventures and small-scale industries.
In this blog, we will explore the complete list of goods and services exempted under GST in 2025. We’ll delve into how these exemptions affect consumers and businesses, providing insights into the strategic objectives behind these policies and their impact on the broader economy.
What is the GST Exemption Limit?
GST exemption limits vary for businesses dealing in goods and services. Any business with turnover below these limits is not required to register for GST but can opt for voluntary registration.
- Goods: ₹40 lakh annual turnover (₹20 lakh for special category states).
- Services: ₹20 lakh annual turnover (₹10 lakh for special category states).
Businesses below these limits do not need GST registration but can register voluntarily.
However, they can choose to register voluntarily to avail benefits like input tax credit and improved business credibility. Here is a complete list of sector-wise GST exempted limits in India with a basic focus on some of the services, rent and profession wise exemption limits.
| Category | GST Exemption Limit | Details |
| Goods Suppliers | ₹40 lakh (₹20 lakh for special category states) |
Businesses selling goods below this limit are GST-exempt.
|
| Service Providers | ₹20 lakh (₹10 lakh for special category states) |
Service providers below this limit do not need GST registration.
|
| Rental Income (Commercial & Residential) | ₹20 lakh |
Landlords earning below this limit are GST-exempt.
|
| Professional Services (Doctors, Lawyers, etc.) | ₹20 lakh (₹10 lakh for certain states) |
GST not applicable for professionals below this threshold.
|
Types of GST Exemptions
- Absolute Exemptions: No GST in all cases (e.g., fresh vegetables, blood donations).
- Conditional Exemptions: GST exempt only under certain conditions (e.g., hospital room charges below ₹5,000/day).
- Non-Taxable Supplies: Not covered under GST laws (e.g., petrol, alcohol).
These exemptions help reduce tax burden and improve affordability.
List of GST-Exempt Goods in India
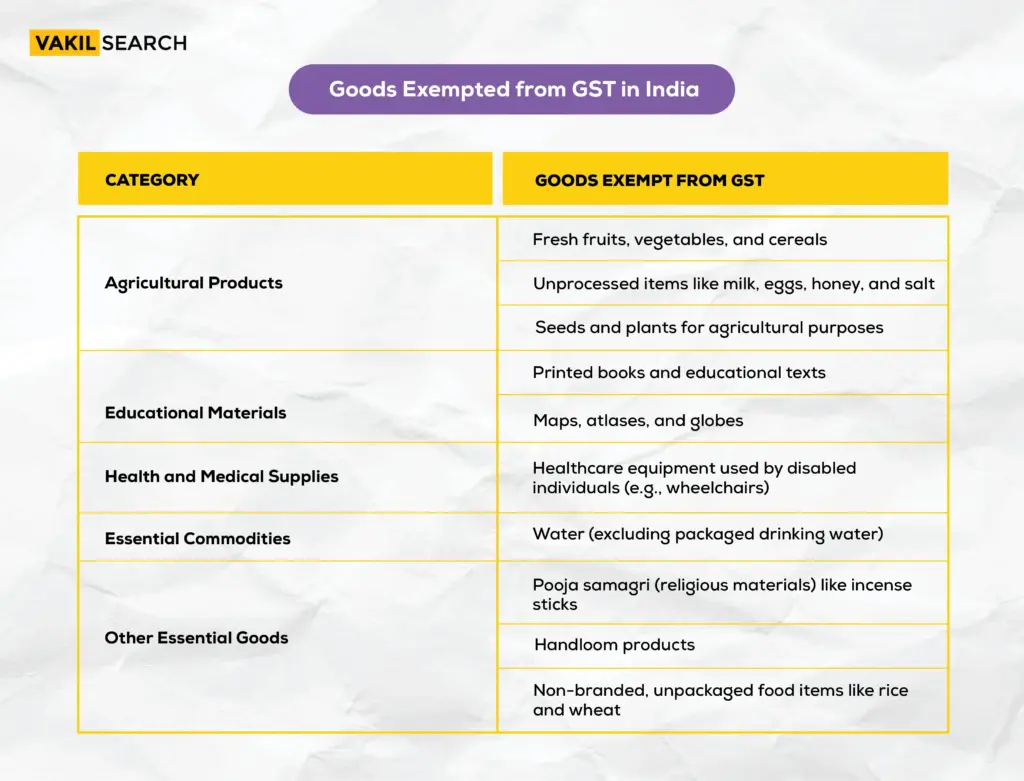
| Category | Exempt Goods |
| Agricultural Products | Fresh fruits, vegetables, milk, eggs, honey, seeds |
| Educational Materials | Printed books, maps, globes |
| Medical & Healthcare | Blood, wheelchairs, essential healthcare equipment |
| Essential Commodities | Water (non-packaged), incense sticks, handloom products |
| Unbranded Food Items | Rice, wheat, pulses (non-packaged) |
List of GST-Exempt Services in India
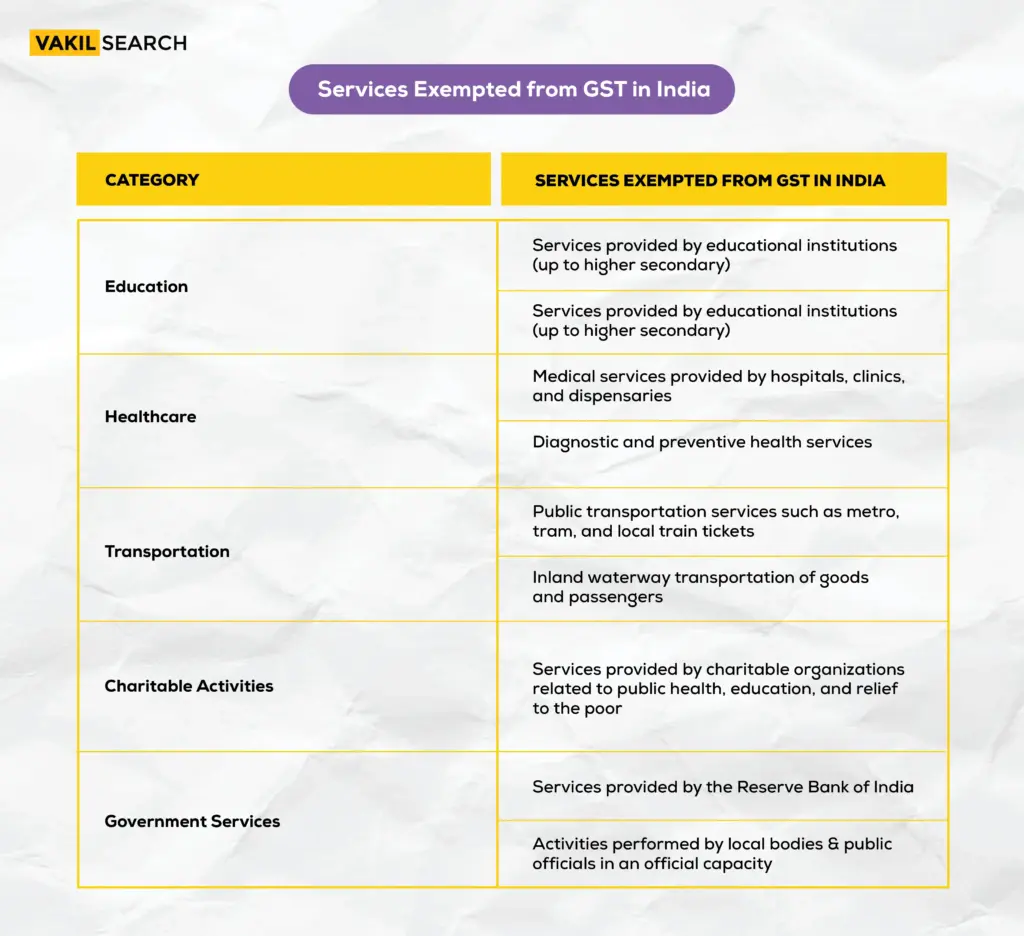
| Category | Exempt Services |
| Education | Schools, colleges, vocational training |
| Healthcare | Hospitals, clinics, diagnostic services |
| Transportation | Metro, tram, local trains, inland waterway transport |
| Charitable Services | NGOs, religious organizations, social welfare |
| Government Services | RBI operations, public administration |
What is an Exempt Supply Under GST?
Exempt supplies under GST are critical to comprehend for businesses aiming to navigate GST compliance efficiently. These supplies are transactions where no GST is applied, influencing both the pricing strategy and tax obligations of businesses.
-
Definition of Exempt Supplies: Exempt supplies are defined as transactions on which the GST rate is zero. This classification ensures that no GST is charged on these transactions, thereby reducing the cost burden on the consumer and eliminating the duty of the supplier to collect GST on such sales.
-
Categories of Exempt Supplies: Exempt supplies under GST fall into three distinct categories:
- NIL Rated Supplies: These are items or services taxed at a 0% rate, essentially leading to no GST being levied despite being part of the taxable universe.
- Legislatively Exempt Supplies: Certain goods and services are exempt from CGST or IGST under specific notifications amending Section 11 of the CGST Act or Section 6 of the IGST Act. This exemption is granted based on socio-economic factors or public interest considerations.
- Non-Taxable Supplies: Defined under Section 2(78) of the CGST Act, these include items like alcoholic beverages for human consumption, which are outside the purview of GST by law.
-
Implications for Businesses: For transactions classified as exempt supplies, businesses are not allowed to charge GST, thereby directly affecting the final price consumers pay. Additionally, Input Tax Credit (ITC) for taxes paid on inputs used to manufacture or supply these exempt goods or services cannot be claimed. This has significant implications for cost structuring and pricing strategies within businesses.
-
Distinction from Zero-Rated Supplies: It’s crucial to distinguish exempt supplies from zero-rated supplies. Zero-rated supplies, such as exports or supplies to SEZs, are also taxed at 0% but allow businesses to claim ITC. This differentiation helps businesses in planning their tax strategies more effectively, especially those engaged in international trade or supplying to special economic zones.
GST Exemption for Startups
Startups should be aware of GST exemption limits and conditions to determine whether registration is necessary. Below are key points to consider:
- No GST Registration Needed if turnover is below ₹40 lakh (goods) or ₹20 lakh (services).
- Startups dealing only in exempted goods/services also do not require GST registration.
- Voluntary GST registration can help avail Input Tax Credit (ITC) benefits.
GST Exemption for Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
GST Exemption for SEZs: All supplies to SEZs are treated as exports and qualify for GST exemption. Suppliers can either:
- Use a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) to avoid IGST and claim Input Tax Credit (ITC), or
- Pay IGST and claim a refund later.
If an SEZ sells goods/services to a Domestic Tariff Area (DTA), it is treated as an export, and taxes apply to the recipient, not the SEZ. On the other hand, if an SEZ is providing goods or services to a Domestic Tariff Area (DTA), such a transaction is considered an export to the DTA. In this scenario taxes and tariffs are only bearable by the DTA recipient and not the SEZ itself.
GST Exemption for Healthcare Professionals
The GST Council clarified that Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) services provided by doctors are exempt from GST as they fall under healthcare services.
In addition, the GST on ostomy and orthopedic appliances which will include artificial slices has also been reduced from the previous rate of 12% to 5%. Biomedical waste treatment services provided to hospitals and clinics attract 12% GST, but service providers can claim Input Tax Credit (ITC).
GST Exemption for Co-operative Societies
Co-operative societies undertaking activities related to agriculture, banking, and lending to their members are eligible for GST exemptions. These exemptions facilitate co-operatives in providing these services to their members with no increase in costs due to taxes.
GST Exemption from Registration
Specific persons and organizations, for example, farmers, are not mandated to register for the Goods and Services Tax. Also, individuals providing NIL Rated or Exempt goods like fresh milk do not have to register for GST. Moreover, participants of activities that are not covered by VAT such as supplying petroleum products do not require to register for VAT.
Turnover-Based Exemptions
Certain types of businesses and service providers, however, may also qualify for GST exemption depending on their annual turnover.
- Goods: Any business with an aggregate turnover not exceeding ₹40 lakh is not required to those provisions of the GST Act that seek registration.
- Services: Service providers with an annual turnover of less than ₹20 lakh are not liable to register for GST.
- Special Category States: For special category states, the threshold limits are further decreased to ₹20 lakh for trade in goods and ₹10 lakh for trade in services.
Therefore, the comprehension of these turnover-based exemptions is very important for these companies to ease the burden of tax compliance on them.
Exemption for Agriculturists
- Individuals involved solely in furnishing unrefined agricultural produce are not required to obtain gst registration.
- This exemption aids in lowering the tax liability for farmers thereby promoting growth within the agricultural sector.
- This exception alleviates the strain of the burdening process on the farmers and ensures that there is no extra tax burden imposed on them.
What Are the Reasons for Exemption Under GST?
GST exemptions are based on policy objectives, socio-economic factors, and administrative ease. Here are the key reasons why certain goods and services are exempt from GST:
- Public Welfare: Essential items like basic food (rice, milk), healthcare, and education are exempt to ensure affordability.
- Small Business Support: Businesses with low turnover benefit from exemptions or lower rates to reduce compliance burdens.
- Export Promotion: Exports are zero-rated to keep Indian goods and services competitive in global markets.
- Interstate Trade Facilitation : Certain interstate supplies are exempt or taxed at lower rates to encourage smooth trade.
- Agriculture Growth: Many agricultural products and services are exempt to support farmers and rural development.
- Government Operations: Services by government bodies or local authorities are exempt to prevent double taxation.
- Financial Services: Specific financial services, such as banking and insurance, have special GST rules or exemptions.
- Cultural & Religious Exemptions: Goods/services used for charitable, religious, or cultural activities may be exempt.
- Simplified Tax Administration: Certain exemptions make GST compliance easier for businesses and tax authorities.
- Smooth Transition: Temporary exemptions or lower rates help businesses adapt during policy changes or GST implementation.
How Are GST Exemptions Granted?
GST exemptions are determined by the Central and State Governments to support public welfare and economic growth. The process involves:
- Official Notifications – Exemptions are formally announced through government notifications, ensuring transparency.
- GST Council Recommendations – The GST Council, consisting of Central and State representatives, must recommend any exemption before implementation.
- Special Orders – In rare cases, exemptions may be granted through special orders for unique circumstances.
Here is the key notifications and updates on GST exemptions, including recent council decisions and procedural changes for compliance:
Key Notifications and Updates on GST Exemptions
Differences Between Exempt, Nil-Rated, Zero-Rated, and Non-GST Supplies
| Type | Definition | Input Tax Credit (ITC) | Examples |
| Exempt Supplies | Goods/services not taxed under GST | Not Allowed | Fresh fruits, educational services |
| Nil-Rated | Taxed at 0% GST but still under GST law | Not Allowed | Grains, jaggery, salt |
| Zero-Rated | Export & SEZ supplies taxed at 0% | Allowed | Exported goods, SEZ supplies |
| Non-GST | Items outside GST framework | Not Applicable | Alcohol, petroleum products |
Conclusion on GST Exemptions
In conclusion, GST exemptions serve as a strategic tool to bolster economic growth and societal welfare by making essential goods and services more accessible and affordable. By extending these exemptions to crucial sectors like agriculture, healthcare, education, and supporting small businesses, the government facilitates significant social and economic benefits.
These policies not only alleviate the financial burden on consumers but also promote the sustainability of vital services and encourage entrepreneurial initiatives. As we move forward, understanding and leveraging these exemptions will be key to maximizing their positive impacts on both the market and the community.
Need expert advice on GST exemptions and GST compliance? Our professionals provide tailored solutions for businesses. Contact us today for a free consultation!
FAQs on GST Exemptions
Businesses with an annual turnover below ₹20 lakh (₹10 lakh for special category states) are exempt from GST registration. Additionally, agriculturalists, specific goods/services, and entities under GST exemption notifications do not require GST registration.
The GST exemption limit is ₹40 lakh for goods suppliers and ₹20 lakh for service providers. In special category states, the limits are ₹20 lakh for goods and ₹10 lakh for services.
If your turnover is below the GST threshold, you are not required to charge GST. However, if you voluntarily register, you must charge GST and comply with all regulations.
The minimum turnover for GST registration is ₹40 lakh for goods suppliers and ₹20 lakh for service providers. For Northeastern and hill states, it is ₹20 lakh for goods and ₹10 lakh for services.
GST turnover includes total sales, exports, exempt supplies, and inter-state sales. It excludes GST paid and inward supplies under reverse charge. Add all revenue sources to determine total turnover.
Check your aggregate turnover for the financial year, including all taxable, exempt, and export sales. If it exceeds the ₹40 lakh (goods) or ₹20 lakh (services) limit, GST registration is mandatory.
Yes, GST is not required if your annual turnover is below ₹20 lakh for services or ₹40 lakh for goods. However, you may opt for voluntary registration to avail input tax credit benefits.
For goods suppliers, the GST registration limit is ₹40 lakh (₹20 lakh for special category states). For service providers, the limit is ₹20 lakh (₹10 lakh for special category states). Who Are Exempted from GST?
What is the Turnover Limit for GST Exemption?
Can I Charge 0% GST When My Turnover is Less Than 20 Lakhs?
What is the Minimum Turnover for GST?
How to Calculate GST Turnover Threshold?
How to Determine if Your Business Meets the GST Threshold?
Is GST Not Required for Below 20 Lakhs?
Is the GST Registration Limit 20 Lakhs or 40 Lakhs?







